In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most transformative innovations across various industries. What started as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies has now evolved into a versatile tool for enhancing security, transparency, and efficiency in business operations.
Companies of all sizes are exploring and adopting blockchain not just for its technical capabilities, but also for the competitive advantages it offers. From secure data management to streamlined processes and increased trust among stakeholders, blockchain is reshaping how businesses operate and create value. This post explores the key reasons why companies are choosing blockchain and how its unique features are driving change across industries.
Why do companies choose blockchain?
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, making it an attractive solution for companies across various industries. One of the primary advantages is security, as blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to protect data by forming a chain where each block is linked to the previous one. Altering a block would require changing all subsequent blocks, a nearly impossible task without control over most of the network. The decentralized nature of blockchain also reduces the risk of attacks by eliminating a single point of failure.
Another key advantage is transparency. Every transaction is recorded in a public ledger, accessible to all participants, ensuring that transactions can be easily verified and reducing the risk of fraud. This openness fosters trust among participants and encourages accountability. Additionally, blockchain’s traceability allows for the precise tracking of assets, which is especially valuable in supply chains, where products can be traced from their origin to the end consumer.
Blockchain also improves efficiency through smart contracts, which are self-executing programs that automate contract terms, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing errors. This streamlining of processes is particularly effective in financial transactions and supply chain management. Moreover, blockchain enables direct peer-to-peer transactions, further cutting costs and reducing dependence on third-party intermediaries.
The immutability of blockchain data ensures that once information is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, making it a reliable option for storing sensitive data like financial records and legal documents. Furthermore, adopting blockchain can enhance a company’s innovative image, attracting investors and partners interested in cutting-edge solutions. However, the use of blockchain must be purposeful and provide real business benefits to justify its adoption.
By combining security, transparency, traceability, efficiency, and the potential for innovation, blockchain is transforming how companies manage digital assets.
Blockchain across industries
Nowadays, blockchain has many applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Below are examples:
- Supply chains: Companies like Walmart and Maersk use blockchain to track products from manufacturer to consumer. This increases transparency and helps to identify the sources of problems quickly.
- Healthcare: Blockchain is being used to store and share medical data securely. For example, the MedRec project allows patients to control access to their medical records.
- Voting: Some countries, including Estonia, are experimenting with blockchain-based electronic voting systems to improve the security and transparency of elections.
- Copyright protection: Platforms like Mycelia use blockchain to protect musicians’ rights, ensuring fair royalty distribution.
- Real estate: Some countries, such as Georgia, use blockchain to register real estate titles, simplifying the process and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Insurance: Companies like AXA use smart contracts on blockchain to automate insurance claims, such as flight delays.
- Education: Blockchain is being used to verify academic degrees and certificates. MIT is issuing digital diplomas using technology.
- Energy: Projects like Brooklyn Microgrid allow neighbors to trade solar power directly using blockchain.
- Philanthropy: Organizations are using blockchain to increase the transparency of donations and how they are used.
Risks of using blockchain
Despite its many advantages, there are important risks to consider when adopting blockchain technology:
- Technological complexity: Implementing and maintaining blockchain systems requires specialized knowledge and skills that existing staff may need to gain.
- Scalability: Some blockchain networks face performance issues as the number of transactions increases.
- Energy consumption: High energy consumption can be an environmental and economic issue, especially for blockchains that use a Proof of Work algorithm (like Bitcoin).
- Legal uncertainty: Legislation in many countries needs to keep pace with the technology, creating legal risks.
- Security: While the blockchain itself is considered secure, vulnerabilities may exist in smart contracts or interfaces that interact with it.
- Transaction irreversibility: Errors in transactions or smart contracts may be irreparable due to the immutability of the blockchain.
- Data privacy: Blockchain transparency may conflict with data privacy requirements.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating blockchain with a company’s existing IT systems can be difficult and expensive.
- Implementation cost: The initial investment in developing and implementing blockchain solutions can be significant.
- Community dependency: The success of public blockchains depends on the activity and support of the developer and user communities.
Examples of successful Blockchain implementations
#1 IBM Food Trust
IBM Food Trust uses blockchain to enhance transparency and traceability in the food supply chain. By recording each step of the supply chain on a blockchain, IBM Food Trust allows stakeholders to track the origin and movement of food products in real time. This has led to reduced fraud, quicker recalls in case of contamination, and increased consumer trust. For instance, Walmart has reported significantly faster tracking of produce, which has improved food safety and reduced waste.
#2 DeBeers
DeBeers, a leading diamond company, utilizes blockchain to ensure the ethical sourcing of diamonds. Through their platform, Tracr, DeBeers tracks each diamond from mine to market. This system helps to verify that diamonds are conflict-free and meet ethical standards. By leveraging blockchain, DeBeers has strengthened its commitment to ethical practices and enhanced consumer confidence in its products.
#3 Ethereum-based Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms
DeFi platforms like Uniswap and Compound, built on Ethereum, have revolutionized traditional financial systems by offering decentralized trading, lending, and borrowing services. These platforms eliminate intermediaries, provide more accessible financial services, and often offer better rates than traditional financial institutions. By using smart contracts on Ethereum, these DeFi applications offer transparency, security, and efficiency in financial transactions.
Comparing Blockchain platforms
#1 Ethereum
Ethereum is one of the most popular blockchain platforms for developing decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. It offers a robust ecosystem with extensive developer support and a wide range of existing dApps. Ethereum is ideal for projects requiring a mature platform with established standards, though it can face scalability issues and higher transaction fees due to network congestion.
#2 Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
Binance Smart Chain is known for its high performance and low transaction costs. It is compatible with Ethereum’s tooling and offers a faster and more cost-effective alternative for deploying smart contracts and dApps. BSC is a good choice for projects that need high throughput and lower fees, though it is less decentralized compared to Ethereum.
#3 Polygon (formerly Matic Network)
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum that aims to improve scalability and reduce transaction costs. It offers a range of solutions, including sidechains and rollups, which enhance Ethereum’s scalability while retaining compatibility with its ecosystem. Polygon is suitable for projects looking to benefit from Ethereum’s security while achieving better performance and lower fees.
#4 Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is an enterprise-grade blockchain platform designed for private and permissioned networks. It focuses on providing modular and customizable solutions for businesses. Fabric is ideal for projects requiring a private blockchain with advanced data privacy and permissioning features, making it suitable for enterprise use cases and complex supply chain applications.
Choosing the right blockchain platform depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as scalability, transaction costs, security, and ecosystem compatibility. Each platform offers distinct features and benefits, so understanding your project’s needs is crucial in selecting the most suitable solution.
Our experience in developing Blockchain-based projects
At IT-Dimension, we have extensive experience in developing innovative blockchain-based solutions that address real-world challenges across various industries. Below are a few highlights.
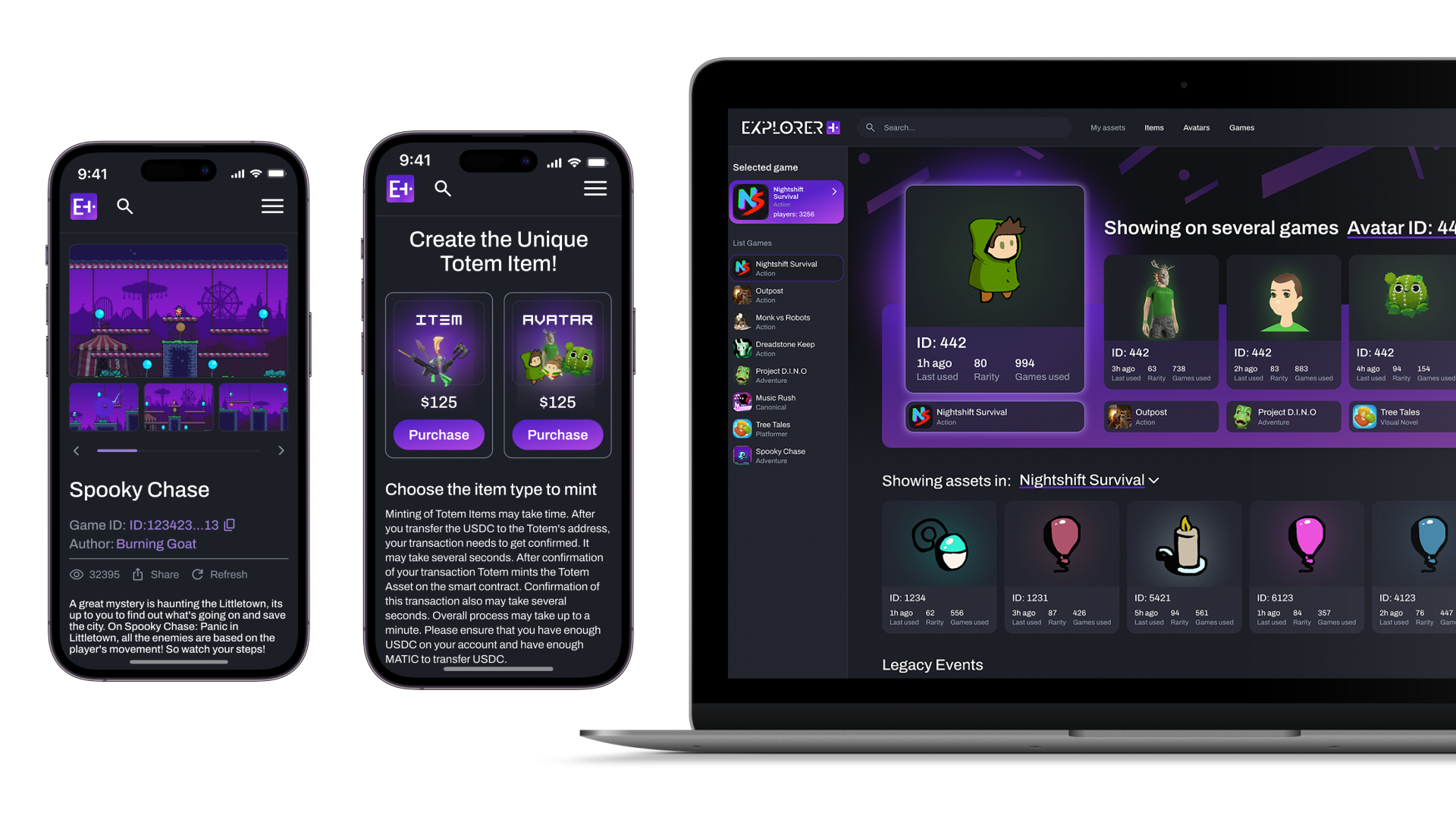
Totem
We utilized blockchain and NFT technology to enable true ownership and exchange of unique in-game assets like avatars and weapons. Players can use these assets across multiple Totem games, creating a seamless experience with full ownership of virtual items.
Totem blockchain-based indie gaming platform
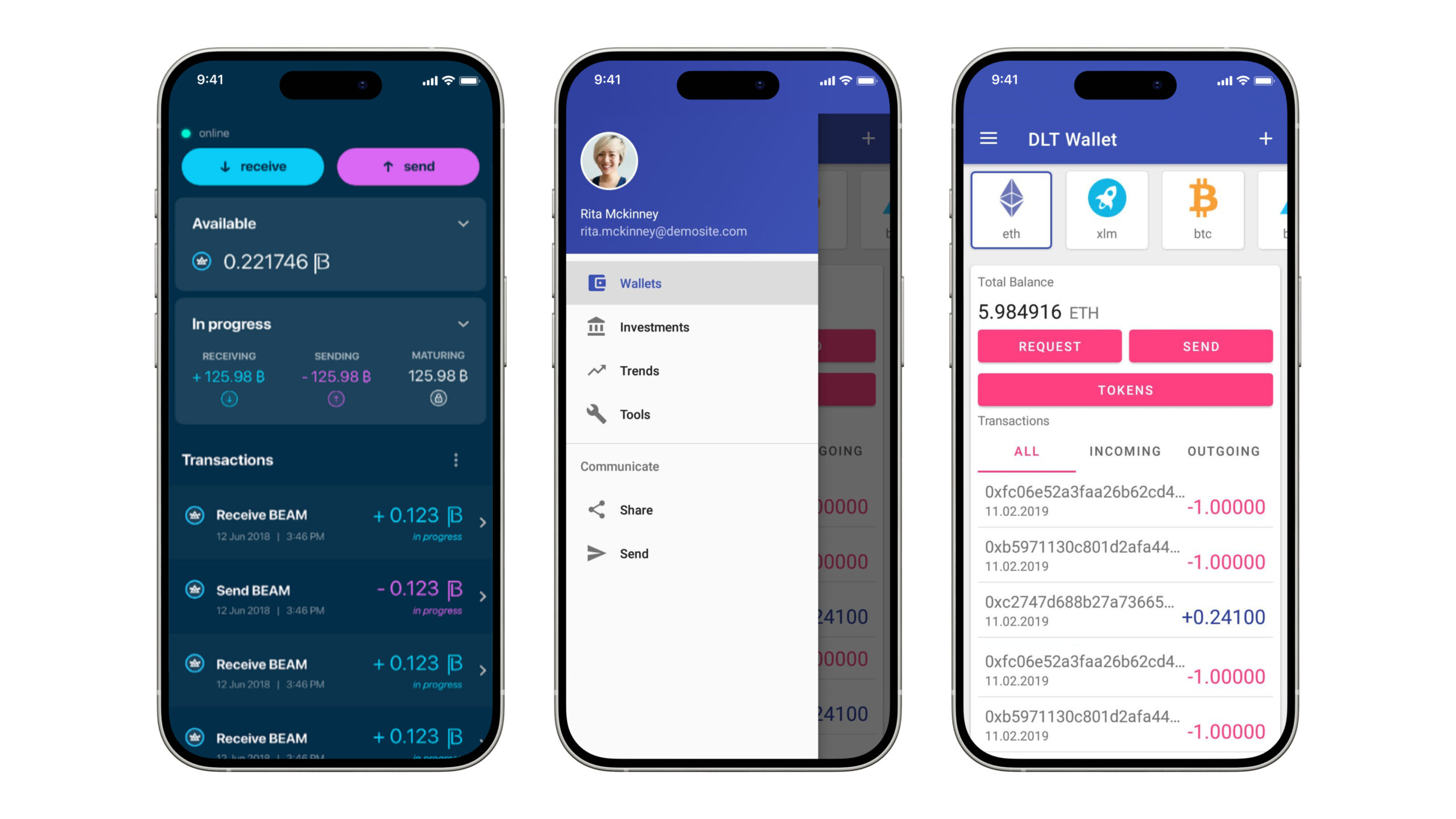
Beam and DLT wallets
We developed the Beam wallet for Beam blockchain, supporting transactions, history tracking, and QR code generation. The DLT Wallet for Android supports multiple cryptocurrencies and ERC20 tokens, providing all necessary wallet functionalities such as sending, receiving, and transaction history.
Beam and DLT mobile cryptocurrency wallets
Conclusion
Blockchain offers transformative benefits that go far beyond its initial association with cryptocurrencies. Companies across various industries are leveraging this technology to enhance security, improve transparency, streamline processes, and reduce costs by eliminating intermediaries. Blockchain opens up new possibilities for innovation and growth in logistics, healthcare, finance, government, and more.
However, as with any technology, it’s important to carefully assess the specific needs of your business and select the right platform and approach, since Blockchain adoption comes with many challenges:
- Technical complexity and high development costs;
- Scalability and energy efficiency issues;
- Legal uncertainty in many jurisdictions;
- The need to integrate with existing systems.
By understanding whether to adopt Blockchain, as well as its benefits and challenges, companies should make informed decisions that lead to long-term success. An even more important question here is how to implement blockchain for your business in a way that brings the greatest benefit to the company.
If you’re looking to explore blockchain solutions, IT-Dimension team is ready to guide you through the development process, ensuring a tailored approach that meets your needs.
Reach out to discover how blockchain can revolutionize your business.
Links:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blockchain
https://academy.binance.com/en/glossary/blockchain
https://www.ibm.com/topics/benefits-of-blockchain
https://www.skylineuniversity.ac.ae/knowledge-update/lifestyle-and-trends/blockchain-applications-in-e-government